A report about the Pangea proposal for a nuclear waste dump in Australia.
Recognition we can all see
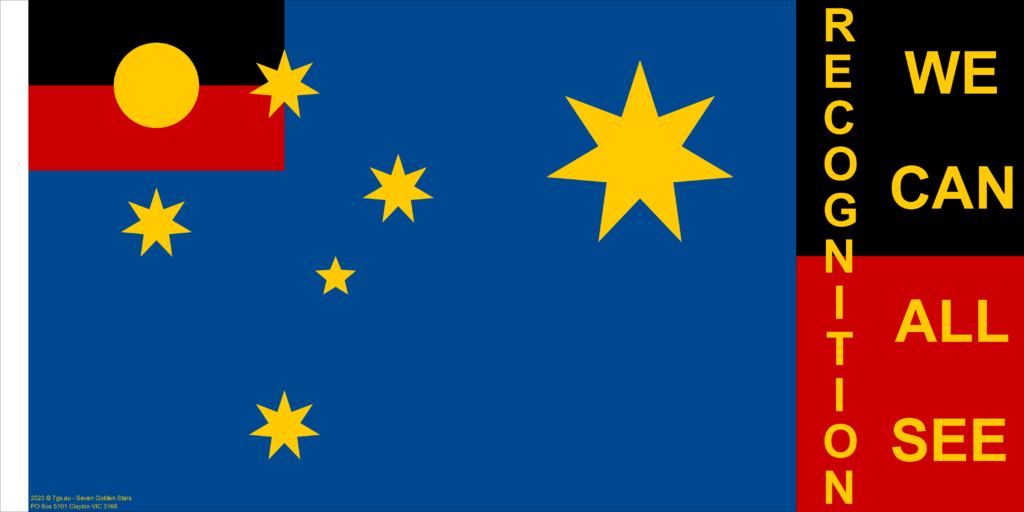
Recognition

Traditional owners win court case to stop nuclear waste dump in South Australia
“Traditional owners opposing the federal government’s plan for a nuclear waste dump on their land in South Australia have had a major win, with a court ruling the facility can’t be built.
The Barngarla people were jubilant outside the federal court in Adelaide on Tuesday after justice Natalie Charlesworth said the commonwealth’s decision to build the dump near Kimba would be set aside.”

Introducing Seven Golden Stars
Seven Golden Stars is the name of an Australian flag where the Aboriginal flag replaces the Union Jack.
It is a flag that symbolises the sovereignty of Australians and honours the First Nations, who have lived sovereign in Australia for over 60,000 years.
We do not need to change the Constitution to recognise the First Nations of Australia.
The sun will still rise in a hundred years hence, regardless of the referendum result.
The flag takes the Southern Cross and Federation Star from the defaced British Ensign and rearranges them symmetrically.
The stars and background colours are Australia’s national colours: at first blue and gold, and now green and gold.

Seven Golden Stars in blue and gold.
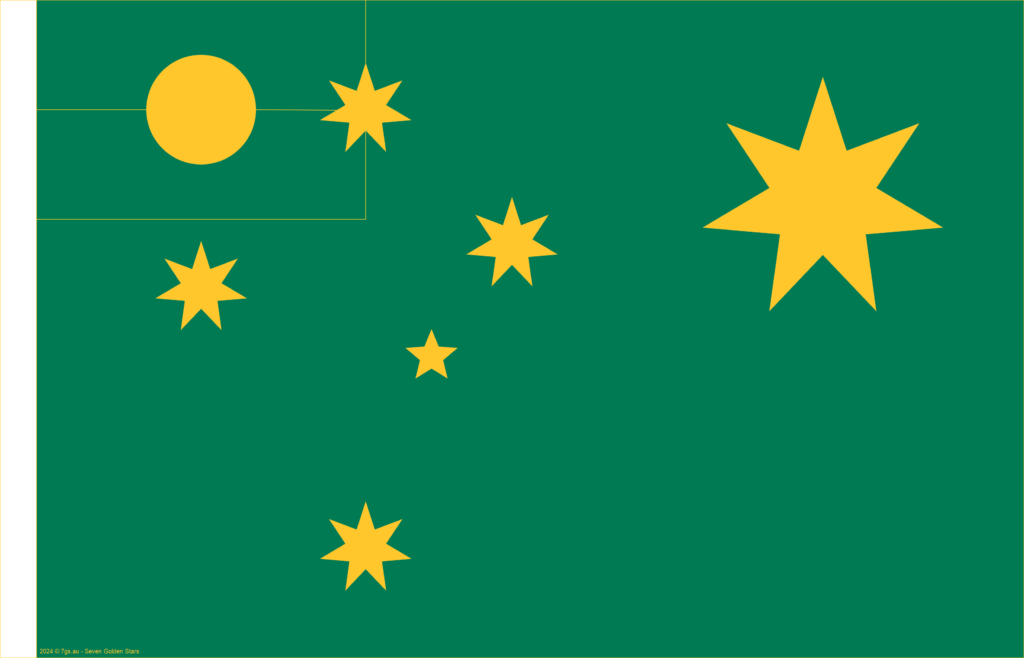

Seven Golden Stars in green and gold.
There are many versions and varieties of this flag design.
The designs are by Robert Vose.
Referendum (Machinery Provisions) Amendment Bill 2022
Referendum (Machinery Provisions) Amendment Bill 2022
Proposed changes for a referendum
https://www.smh.com.au/politics/federal/reconciliation-will-be-damaged-if-voice-fails-burney-20221117-p5bz8i.html
…The federal government has committed to holding the referendum during the 2023-24 financial year, with the final date yet to be determined by the cabinet. It has been working closely with a working group of Indigenous leaders who, in a meeting last week, canvassed changes to the Referendum Machinery Provisions Act 1984 which will be considered by cabinet in the coming fortnight.
One option on the table is to change the act’s requirement for voters to be sent a pamphlet in the post outlining the proposed change to the Constitution, comprising up to 2000 words each on the Yes and No case, and instead make this information available electronically…
Australian of the Year 2023 for NSW
Congratulations to Craig Foster AM for being selected Australian of the Year 2023 for NSW!
How timely!
Imagine having the Australian of the Year from one state as our head of state who would replace the King/Queen in an Australian constitutional republic.
There is still a Governor for NSW. There is still a Governor-General for the Commonwealth. There are still the 5 other state Governors who will all continue to maintain our parliaments and keep them humming along as normal.
There would be a round robin of the states so that once every 7 years each state can share the office of head of state. Let’s say in 2023 it is the turn for a man from NSW, then in 2030 it would be the turn for a woman from NSW to be Australian of the Year.
It would be a ceremonial role. Very public. They would meet foreign presidents, perhaps open sessions of parliament, open shows and events, give presentations and awards at schools, and preside over many other events as the guest of honour.
As head of state they would have the most important and prestigious role of unifying all seven divisible Crowns of Australia, just as the King/Queen does now. No one else can do that. It is a very special role. Only Australia’s head of state has that honour.
In the next few years we could experiment with an election process to select the Australian of the Year in a particular state.
I don’t mean to put Craig Foster under pressure. Having been elected to the ARM leadership this is a great opportunity to explore options for a republic.
One option is to convert an existing institution we are all familiar with, modify it so that it is suitable for the task, and test this as a vehicle for replacing the King/Queen with an Australian to serve a fixed term as our head of state.
https://www.nsw.gov.au/media-releases/congratulations-to-2023-nsw-australians-of-year
Reason for an Australian head of state
What is the main purpose or justification for having an Australian head of state?
It’s interesting that Matt Thistlewaite mentions one of the main roles of an Australian head of state is to defend the Constitution. This can narrow the meaning for the role and also define who could be eligible, the method of selecting that person, and the term in office.
Many people are tasked with protecting the Constitution. The High Court and judiciary interpret the constitution and apply their interpretations through their considerations. They protect the law and defend the constitution.
The vice-regal representatives of the King/Queen have recourse to reserve powers to protect our system of government in the rare situations where a government acts unconstitutionally.
A view that our head of state is there to protect the Constitution would be consistent with a framework that tries to merge the two distinct roles of King/Queen and the Governor-General into the new role of an Australian head of state. This is the framework adopted by the ARM. It is usually based on imitating the way that nearly all other former commonwealth nations have become republics.
There is, however, a problem with that approach. While all other former commonwealth nations (bar one) had only one representative or Governor-General of the King/Queen before becoming republics – Australia is unique in that we have seven representatives of the King/Queen. We have a Governor-General for the Commonwealth and a state Governor for each of the six states respectively. Australia has a one-to-many relationship between the King/Queen and their representatives. Most other commonwealth republics, an example being Ireland, only had a one-to-one relationship. That approach will not work for Australia and our federal system with the Commonwealth and states. We can keep the Governor-General and State Governors as the representatives of an elected head of state for the Australian Federation.
I know there is a better way. I know that the Australian head of state can symbolize the unity and integrity of the Australian Federation within Australia and aboard. I know that the head of state can represent the diversity of the Australian people. We can replace the King/Queen with an Australian as our head of state and the nomination and election process can build our civic society and showcase our values of a fair go. We can share the office of head of state around all the six state and the territories equally. We can do better than what we have now. Australians can feel ownership and pride by taking part in the process of nominating, campaigning, and electing a person as head of state who will personally unify all seven divisible Crowns for Australia’s Federation as a constitutional republic. It will be a ceremonial role, and it will belong to the Australian people. We will own it.
Possible Plebiscite Questions
To determine the preferences of Australians for a transition from a constitutional monarchy to a constitutional republic, many people have proposed a series of plebiscite questions.
Here are three questions which will give us a full range of options.
Question One – Framework
Would you support replacing the King/Queen and Governor-General with an Australian Head of State for the Commonwealth only? Yes/No?
Yes is for a framework proposed by the ARM and Real Republic groups as a suitable framework for a republic.
No is to keep the existing framework as with the constitutional monarchy where the King/Queen is the head of state for the Commonwealth, the six States, and the Territories all at the same time.
Question Two – Model for a republic
What is your preference on the method to select an Australian Head of State:
- Australia’s Head of State appointed by a 2/3 Majority of the Federal Parliament (1999 referendum model)
- Australia’s Head of State selected with a direct election across all of Australia (Real Republic Direct Election model)
- Australia’s Head of State selected with a state-based direct election in a round robin of the six States, and the Territories combined (Federal Crown of Australia model)
- Australia’s Head of State selected with a direct election across all of Australia, where candidates are nominated by Commonwealth and State Parliaments (ARM Australia Choice model)
- Australia’s Head of State to remain as the monarch of the United Kingdom through the line of succession to the British Throne (keep the existing default monarchy).
- The Prime Minister as Head of Government assumes the role when it is needed (no separate person as Head of State)
- None of the above – my preferred option is not listed
Preferential vote with one or more consecutive numbers out of these six options. A vote of 1 is the highest preference, and a vote of 6 is the least preferred.
Question Three – the Crown of Australia
Do you agree to abolish the Crown of Australia? Yes/No
Yes – The Australian Commonwealth, States and Territories will abolish the Crown of Australia in the transition to a republic.
No – The Commonwealth, States and Territories will work with the Governments of the UK and Canada to have the Crown of Australia altered so that the rules for succession to the Crown of Australia are democratic and follow the rules as approved by the Australian people in a successful referendum vote.

